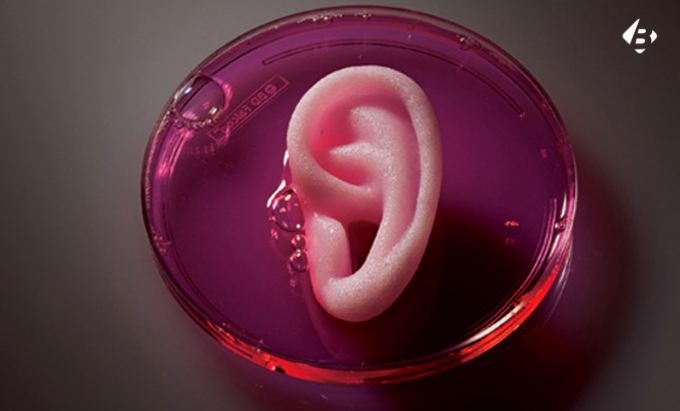
The human body is a masterpiece of intricate design, composed of countless cells and tissues working in perfect harmony. But what if we could engineer this complexity ourselves? With the advent of 3D bioprinting, this once science fiction scenario is rapidly becoming a reality, promising transformative possibilities for the future of medicine.
What is 3D Bioprinting?
3D bioprinting utilizes advanced technology to layer living cells, biomaterials, and other biological components to create functional tissues and organs. Imagine a printer that, instead of ink, uses living cells to build complex structures that mimic the natural architecture and function of human organs. This technology holds immense potential for revolutionizing regenerative medicine, drug discovery, and personalized healthcare.
The Promise of 3D Bioprinting:
- Transplantation Revolution: 3D-printed organs could address the critical shortage of donor organs, offering hope to millions awaiting life-saving transplants.
- Personalized Medicine: Bioprinted tissues could be engineered with a patient’s own cells, minimizing the risk of rejection and paving the way for personalized treatments.
- Drug Discovery and Testing: Bioprinted tissues could be used to develop and test new drugs more efficiently and accurately than traditional animal models.
- Disease Modeling: 3D-printed models of diseased tissues could accelerate our understanding of disease progression and facilitate the development of novel therapies.
From Laboratory to Clinic:
Several exciting advancements are pushing 3D bioprinting closer to clinical application:
- Bioinks: Scientists are developing advanced bioinks composed of various biocompatible materials that provide the necessary support and structure for cell growth and tissue development.
- Vascularization: Printing intricate networks of blood vessels is crucial for supplying nutrients and oxygen to bioprinted tissues, and significant progress has been made in this area.
- Organ Printing Techniques: Researchers are exploring various printing techniques like inkjet, extrusion, and laser-based approaches, each offering unique advantages and challenges.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Despite the immense potential, 3D bioprinting still faces several challenges:
- Scalability: Printing large and complex organs with sufficient vascularization remains a technical hurdle.
- Cost-effectiveness: Current printing processes can be expensive, necessitating further advancements for widespread adoption.
- Regulatory Landscape: Establishing clear regulatory frameworks for clinical trials and approval of 3D-printed organs is crucial for bringing this technology to patients.
The Future of 3D Bioprinting:
The future of 3D bioprinting is brimming with possibilities. With continued research and development, we can expect to see:
- Bioprinted organ transplantation becoming a reality, saving countless lives.
- Personalized medicine tailored to individual patient needs based on their own bioprinted tissues.
- A paradigm shift in drug discovery and testing, leading to faster development of safer and more effective treatments.
Conclusion:
3D bioprinting is not just a technological advancement; it’s a revolution in the making. This transformative technology has the potential to revolutionize medicine, offering hope for a future where organ failure and debilitating diseases become a thing of the past. As researchers and medical professionals collaborate to overcome remaining challenges, we are on the cusp of a new era in healthcare, where bioprinting will rewrite the very definition of what it means to be human.
The prospect of 3D bioprinting shaping the future of medicine is both fascinating and revolutionary. The potential to overcome organ shortages and pave the way for personalized treatments is truly groundbreaking.
The promises of 3D bioprinting, from addressing organ shortages to advancing personalized medicine, highlight its transformative impact on healthcare. Overcoming current challenges could lead to a medical revolution.
The progress in 3D bioprinting is remarkable, bringing us closer to a future where organ transplantation is more accessible and personalized medicine is a reality. The challenges ahead only emphasize the significance of this groundbreaking technology.
The concept of 3D bioprinting introduces a new era in healthcare, offering solutions to organ shortages and opening doors to personalized treatments. Navigating challenges like scalability and cost-effectiveness will be key to realizing this futuristic vision.